What foods are high in lutein, and why would you care? Lutein is a well-known antioxidant vision booster, but it also offers protective benefits for better brain health. New research reveals its role in enhancing brain function, promoting cardiovascular health, and protecting against age-related blindness. The catch? Most people aren’t getting enough. Here’s how this golden antioxidant works—and the delicious foods that can help you get more of it every day.

Key Takeaways
Lutein supplements may help prevent a leading cause of macular degeneration as well as cataracts, which are cloudy patches that inhibit vision.
A major lutein benefit is to protect eye health and support the macula of the eye, but more research is revealing that lutein is also critical for brain health benefits.
Lutein is a fat-soluble antioxidant contained in vegetables and is available in supplement form as well. Studies suggest that most people need to take supplements to benefit.
What Is Lutein?
You've no doubt heard you should eat the colors of the rainbow. It turns out that eating those colors protects your vision while boosting brain blood flow, which in turn protects your brain's cells. There's a direct correlation. And we can attribute that amazing support to lutein and its antioxidant partner in anti-aging, zeaxanthin.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are the two major dietary carotenoids that accumulate in the macula region of the retina, located at the back of the eye, shielding the eyes from harmful blue light and the proliferation of free radicals.
They are powerful antioxidants and carotenoids—pigments found naturally in colorful fruits and vegetables, especially in dark leafy greens like kale, spinach, and collard greens. Carotenoids are yellow and orange pigments found in many vegetables. They were originally isolated in carrots, hence the name, carotenoids.
The carotenoid family, which includes beta-carotene and other carotenoids, is found in dark green, leafy vegetables and other colorful fruits and vegetables.
Xanthophylls are a subgroup of carotenoids. Lutein and zeaxanthin are both xanthophylls, known for their yellow-orange hues and their potent antioxidant properties.
Lutein is often dubbed “the eye vitamin,” because it's highly concentrated in the macula of the eye, where it helps filter harmful blue light and protect against oxidative damage. Lutein is one of the best vitamins for vision health, because it plays a key role in maintaining healthy vision and may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts. Both lutein (and zeaxanthin) must be obtained through dietary antioxidants or supplements, as the body cannot produce them on its own.
Lutein is so heavily concentrated in the retinas of your eyes that it's long been considered an essential component of healthy vision. But the more we learn about lutein, the more we're realizing that it's not only essential for eye health, but also for brain health -- a serendipitous discovery made in 2008.Lutein carotenoids may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and also benefit skin health.
Health Benefits of Lutein
Lutein has many benefits, and they're not all related to the eyes. Besides eye and skin health, the retina is structurally an extension of the brain itself, so it's not surprising that benefits were found to extend to the brain. Then there's the anti-aging benefits to your skin. Perhaps in a similar vein to protecting your eyes from blue screens and blue light, lutein also seems to protect your skin from UV rays.
To sum up, lutein and dietary carotenoids:
Support eye health and protect against age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and other eye diseases.
Protect brain health and cognitive function.
Improve cardiovascular health and lipids
Play a protective role against diabetic retinopathy.

Offers The Best Vision Protection for Sharper, Clearer Eyesight
Eye health is a significant concern of many people as they age, as it has a significant impact on your ability to enjoy life and live independently. Lutein has been shown to reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other eye diseases, including cataracts and diabetic retinopathy.
One way lutein offers eye health benefits is by protecting the macula against harmful blue light and free radicals, as well as reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. Lutein may also protect you from other eye diseases such as glaucoma and retinal detachment, although more research is needed to confirm this.
Higher dietary intake of lutein-rich foods and taking lutein supplements may benefit eye health, especially in older adults and individuals at risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Promotes Better Cognitive Function and Memory
While lutein's role in vision support has been studied for decades, its role for cognitive and brain health emerged in 2008 when a clinical trial found that older adults (ages 60 - 80) supplemented with lutein improved their cognitive performance during the course of the trial. This has sparked a wave of study into lutein's role in cognition.
In addition, analysis of post-mortem brain samples found that lutein is the most predominant carotenoid within the brain. Apparently, both the macula and the brain preferentially slurp up dietary lutein, presumably for very specific purposes.
The macular pigment (MP) in the central area at the back of the eye may act like sunglasses to shield our eyes from damaging blue light from the sun and from electronic devices. The MP density reflects the amount of lutein and zeaxanthin in the macula. Interestingly, a study into matched macula and brain tissues found that macular pigment density was directly related to brain lutein concentrations. Many studies now confirm that older people with higher macular pigment density have higher brain lutein content, and better cognition, memory, language, and learning. [1]
It's also interesting to note that although lutein is not the major carotenoid in our diet, it is the highest concentrated carotenoid in human brain tissue. Lutein and zeaxanthin account for 66 - 77% of the total carotenoid concentration in human brain tissue. They've been found in the hippocampus, cerebellum, and the frontal, occipital, and temporal cortices. Due to their powerful antioxidants and anti-inflammatory benefits, interest in their neuroprotective benefits is growing.
Improves Heart and Metabolic Health
A comprehensive review of seventy-one relevant articles on lutein and heart health, including a total of 387,569 participants, found that higher dietary and circulating lutein levels were consistently associated with lower risk of cardiovascular events, better cholesterol profiles (higher HDL, lower LDL), and less metabolic syndrome.
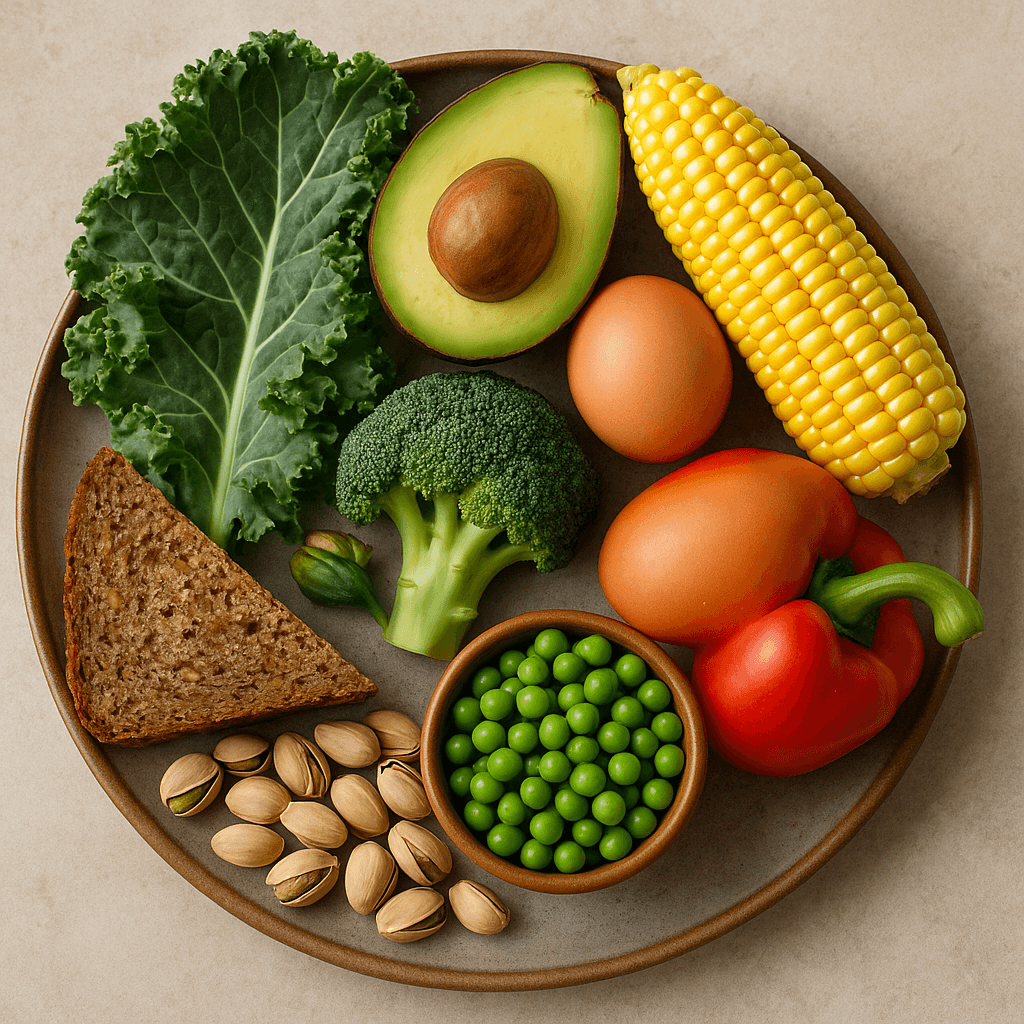
Top 9 Lutein-Rich Foods
Given these astounding vision and brain benefits, lutein's important antioxidant effects, and the negative environmental factors we live with daily, it's very important to get enough lutein. Research shows that most of us only get a tiny fraction of the amount of lutein we need in our daily diet. These could be some of the most important foods you can enjoy as you age, as studies suggest their vital role for good vision and cognition.
Many fruits and vegetables contain lutein, and most of them are low-calorie, offering weight management health benefits while boosting lutein concentration in your bloodstream. It's like going on a diet that lasts a lifetime and provides astounding benefits for human health. And, while you might end up taking a lutein supplement as insurance, getting lutein from eating lutein-rich foods is still an important choice.

So, are you ready to start enhancing your eye health and brain health with nature's bounty of carotenoids and their rich, colorful foods? Here's how to start reaping the benefits of lutein today. Just add these to your daily diet.
Leafy greens, including raw kale, cooked spinach, romaine lettuce, and collards
Other green vegetables, such as broccoli and peas
Yellow and red vegetables such as corn and bell peppers
Eggs (especially yolks, a rich source of lutein and zeaxanthin, as well as vitamin C and other antioxidants)
Sweet potatoes
Honeydew melon
Whole grains and brown rice
Nuts such as pistachios, as well as seeds like sunflower seeds.
Avocados
Bonus Tips To Improve Your Results:
How to Maximize Absorption
Because both lutein supplements and lutein food sources are fat-soluble, it's important to include fat sources with all your lutein consumption to enhance absorption.
Egg yolk is perhaps a perfect lutein food, as it contains healthy fats, as well as lutein. If you want your dark green vegetables or romaine lettuce to promote your lutein levels, include a source of fat, such as olive oil, eggs, or nuts, to enhance these food sources.
Choose Quality Produce and Prepare Thoughtfully
The lutein content of foods varies depending on type, processing, and cooking method, and may be affected by factors such as dietary fiber and other nutrients. A diet lacking in fresh produce, whole foods, and diverse nutrient sources will almost always lead to lower lutein levels. Conversely, a nutrient-rich diet supports better tissue uptake of lutein in both the eyes and brain. Choosing to eat whole, unprocessed foods always helps ensure a higher intake of lutein and other essential ingredients.
Live a Healthy Lifestyle
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and chronic inflammation can deplete antioxidant stores, increasing your body’s demand for lutein and other protective compounds.
How Much Lutein to Consume
How much lutein should you consume? That depends on individual factors including age, health status, and dietary intake, as well as overall nutritional status. Your overall nutrition status means the combination of all the vitamins, minerals, fats, and other compounds you consume, as well as how healthy your digestive system is. Together, that determines how much lutein you actually absorb and benefit from.
The recommended daily intake of lutein has not been established. However, research indicates that 10-20 mg per day may offer optimal health benefits.
More research is needed to determine the optimal dosage and safety of lutein supplements. It's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements, especially if you have a medical condition or are taking any medications.
Real Life Reports From Supplement Takers
Reddit shows how people are benefiting from lutein supplements:
’"Im taking it for my eye health. I have seen a difference so far, but I also have noticed that it has helped imo my brain function better. I would forget words... now I have better clarity, and my vocabulary feels like it’s has gotten better. Reddit
"Way less eye fatigue when I'm working on the computer."
"Lutein supplements beat real food for potency and immediate effects, I've verified this on my eyesight."
And then there are those who prioritize lutein intake via food sources:
"I took 1.5 bunch greens along with various fruit per day in three quarts of green smoothie, and after one to two months I no longer needed the readers I needed for years."
Summary
Lutein is a fat-soluble carotenoid found in colorful fruits, vegetables, and egg yolks that plays a critical role in protecting vision, especially the macula, from blue light and oxidative damage. It may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cataracts, and other eye diseases, while also supporting brain health, cognitive function, and cardiovascular health. Despite its importance, most people consume far less than the optimal daily amount. Eating lutein-rich foods—such as leafy greens, bell peppers, eggs, and pistachios—along with healthy fats enhances absorption. While supplements can help fill gaps, whole food sources offer co-nutrients and better bioavailability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What foods have the most lutein?
Foods high in lutein include dark leafy greens like kale, spinach, and collard greens. Other excellent options are egg yolks, peas, corn, zucchini, and avocados. These foods are rich in natural lutein and also provide other eye- and brain-supportive nutrients.
How much lutein do I need daily?
There’s no official Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA), but most studies suggest 6 to 20 mg of lutein per day supports eye and brain health. The average diet provides only 1–2 mg, so increasing your intake through food and/or lutein supplements may offer benefits.
Can lutein improve brain health?
Yes, emerging research indicates that lutein supports cognitive function, memory, and processing speed—especially in older adults. Lutein accumulates in the brain, helping to protect neurons by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Is food better than supplements for lutein?
Whole foods like leafy greens and eggs offer better bioavailability and come with co-nutrients that support absorption. However, lutein supplementation can be beneficial for those who don’t consume enough from diet alone, which is to say, most of us.
How do I absorb lutein better?
Lutein is fat-soluble, so consuming it with healthy fats—like olive oil, eggs, or avocado—greatly boosts absorption. Light cooking (e.g., steaming spinach) can also make lutein more bioavailable without destroying its nutrients.
https://www.incredibleegg.org/nutrition/articles/lutein-the-eyes-and-brains-best-friend/
Foods Highest in Lutein & Dietary Absorption WebMD. (2024). Foods High in Lutein.
Fat Solubility and Absorption Insight. Review of Optometry. (2024). A Look at Lutein.